INSPECTION AND NDT
Neutron Insights leads the future of industrial radiography with advanced Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) technologies through neutron emission and detection.
Our solution surpasses the limitations of conventional X-ray radiography, offering greater penetration capacity in dense materials and precise defect detection in metals and structures.
Our unique technology provides detailed information about the elemental composition of the sample. We redefine the standards of precision and reliability in material inspection, improving the quality and integrity of industrial processes.
HOW DO WE DO IT?
Some examples of our work:
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING![]()
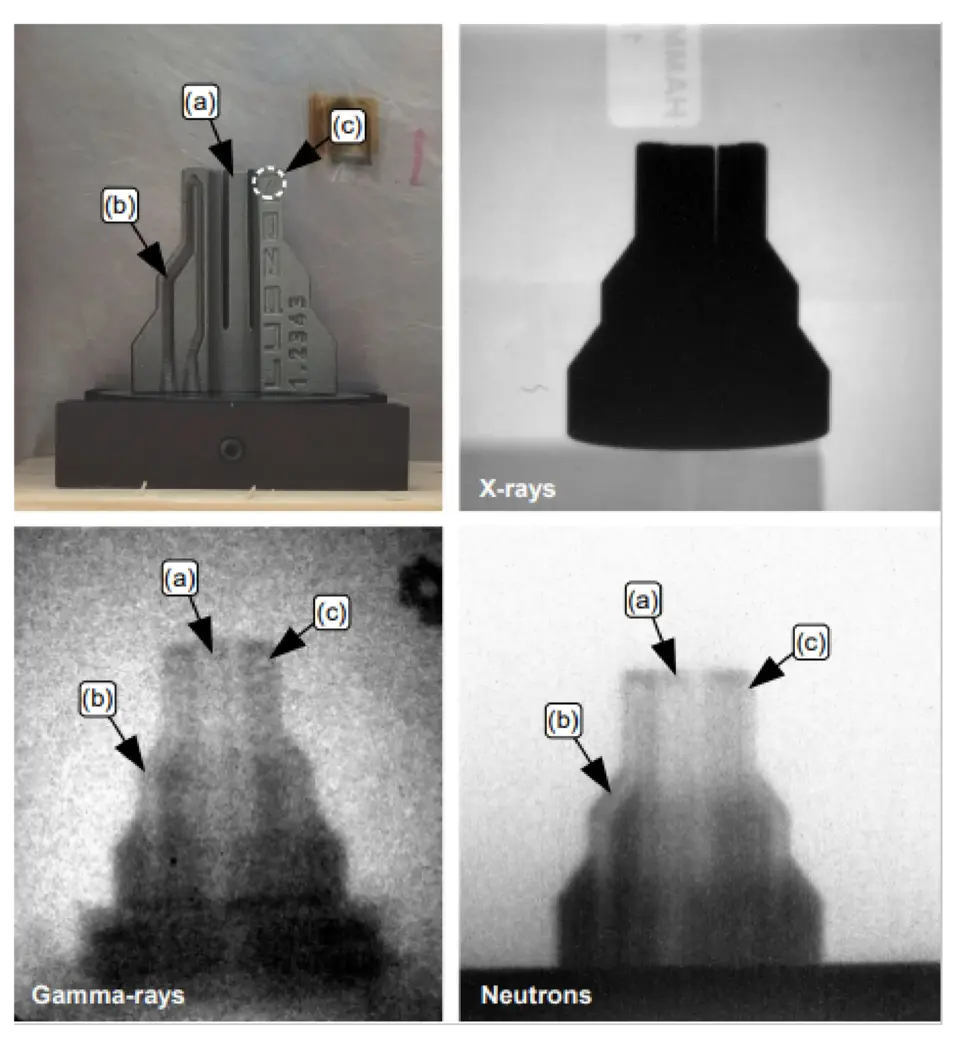
Radiographic image of a 1.2343 steel fuel injector manufactured through 3D printing with the three possible techniques:
-Rayos X
-Rayos Gamma
-Neutrons
Our unique technology provides detailed information about the internal structure of the sample.
We redefine the standards of precision and reliability in material inspection, improving the quality and integrity of industrial processes.


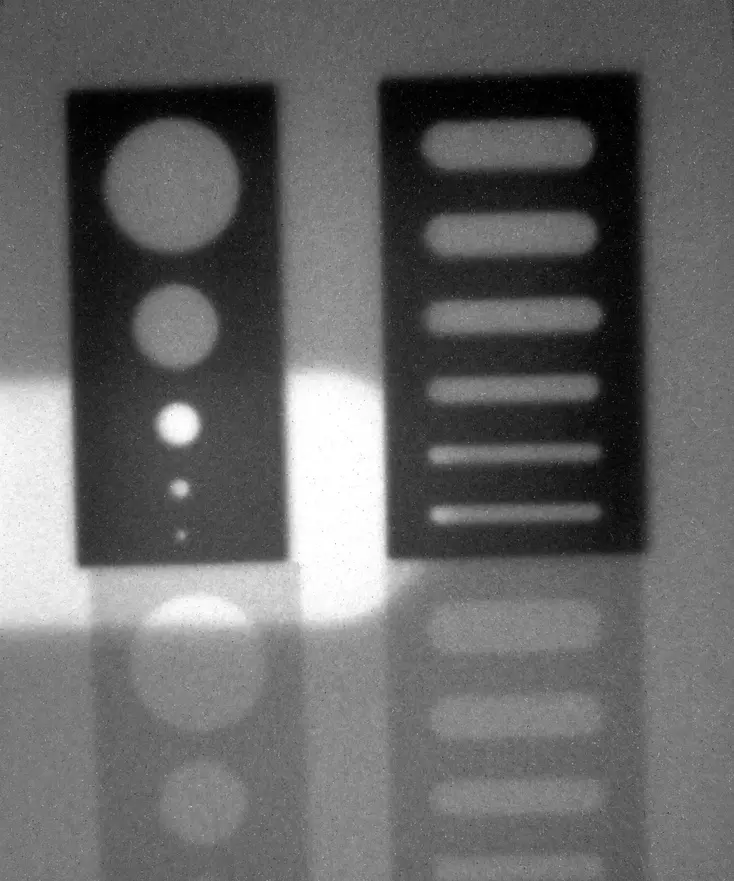
A dissipative part made of 2343 steel using additive manufacturing technology.
Through a three-dimensional analysis, we can clearly visualize the small internal ducts that make up this piece and follow its path within it.
This achievement demonstrates our ability to generate 3D images with precision and detail.
STEEL TUBE![]()
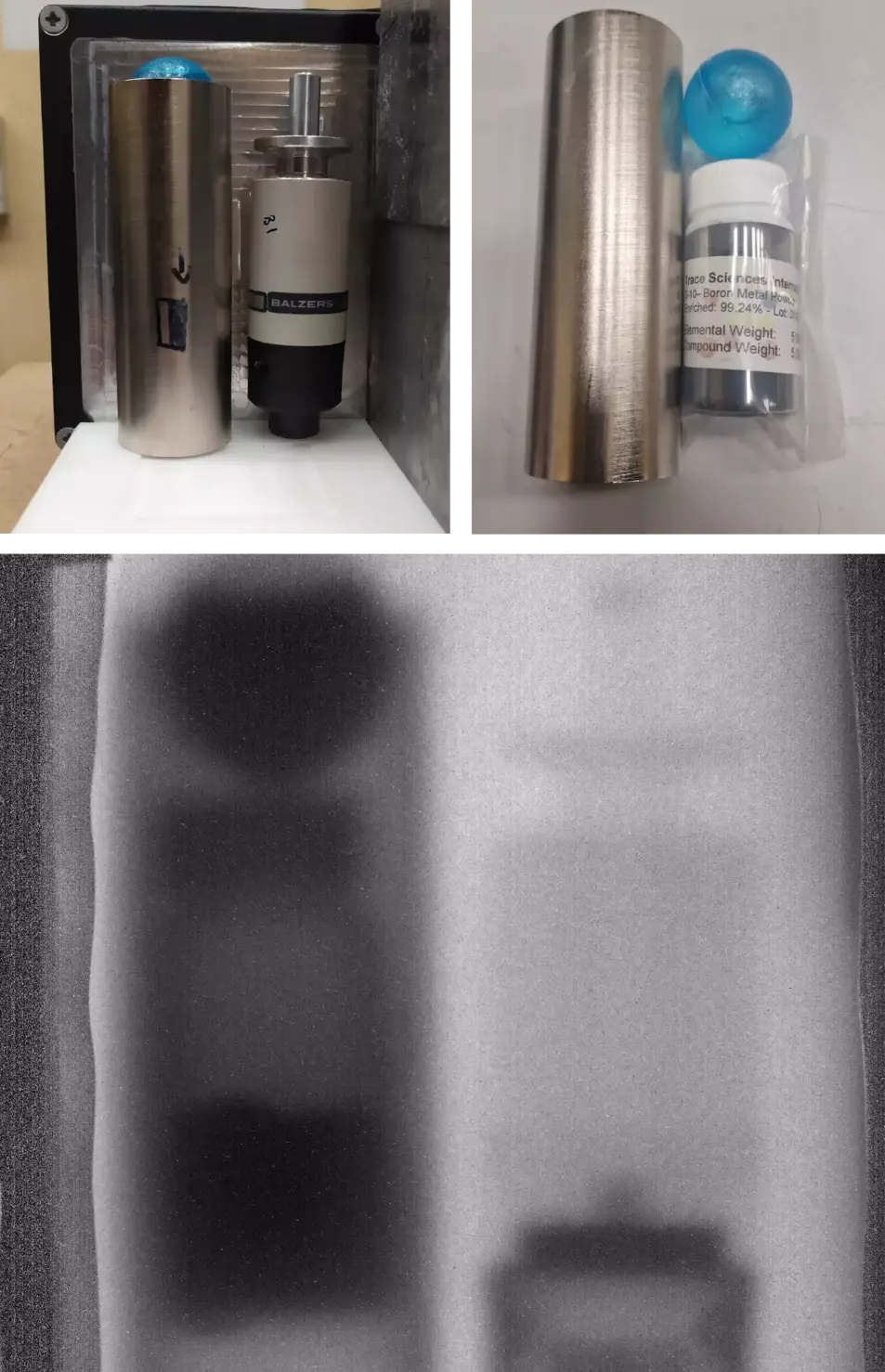

Image of a steel cylinder with materials inside and the head of a pressure sensor. The cylinder is a 3mm thick tube, along with a water-filled blue spherical buoy, and a glass jar containing Boron powder.
It can be seen how the neutron radiography penetrates the steel tube, allowing for a clear distinction of the objects inside, even highlighting light elements such as water, plastic, and boron.
The best option for specific non-destructive testing applications.
We optimize and accelerate manufacturing processes through our services.
Neutron radiographies offer:
– Greater penetration capability
– Better contrast
– Higher sensitivity to different elements
– Less damage to materials
– Increased radiological safety.
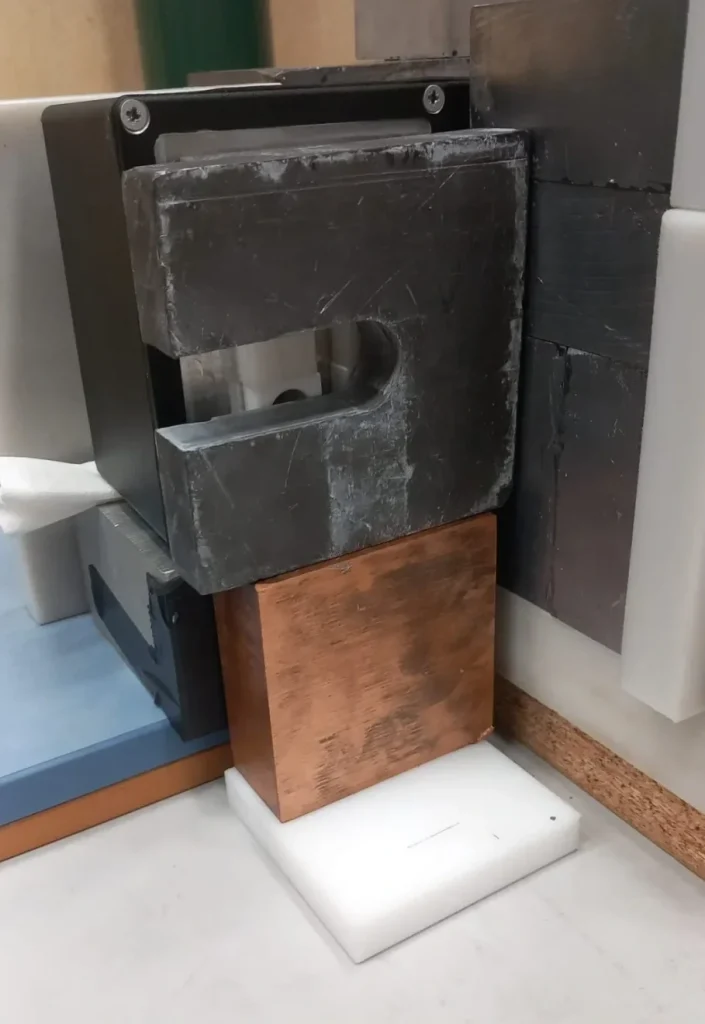
THROUGH THE LEAD![]()
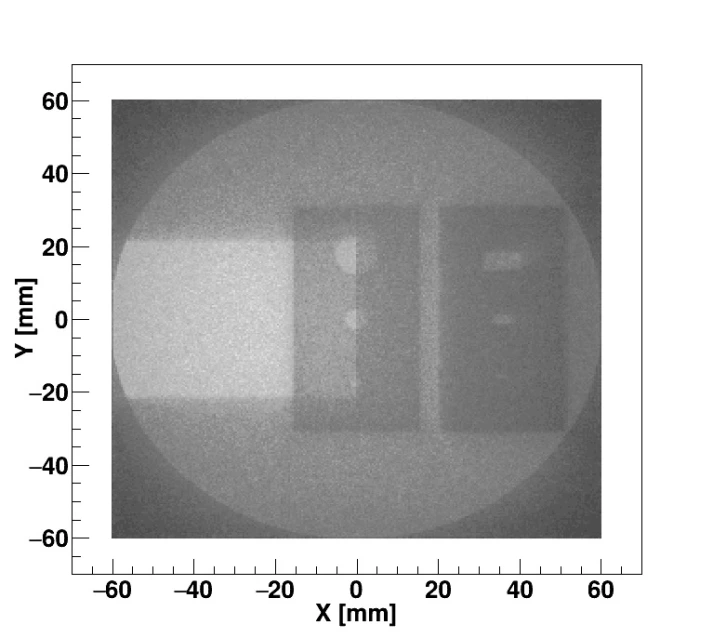
We have also demonstrated how with the neutrons we are able to pass through the lead, and how our systems radiograph with neutrons the Teflon and polyethylene phantoms that are hidden behind that 2.5 cm U-shaped block of Pb.

SIMULATIONS AND DIGITAL TWINS![]()
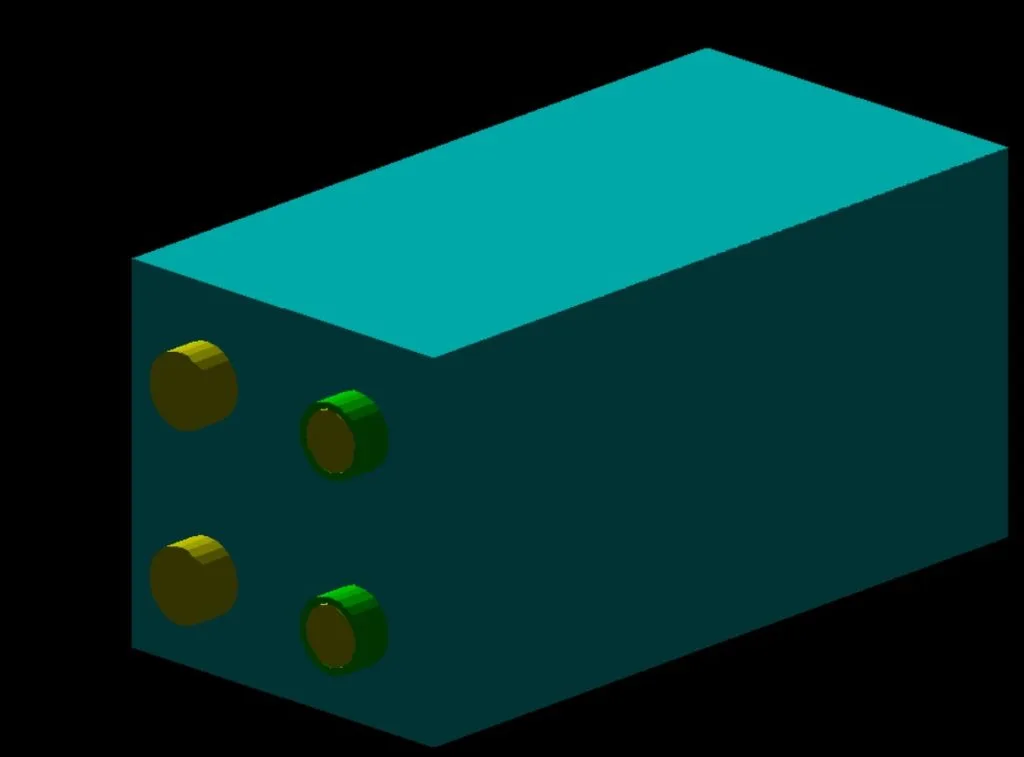
We offer advanced simulation services for NDT inspections using digital twins, allowing for the evaluation of the integrity and performance of components in virtual environments, optimizing both time and resources. This technology facilitates the assessment of parts operating under extreme conditions, simulating environments that are difficult to replicate in real life.
SIMULATIONS AND DIGITAL TWINS
At Neutron Insights we not only use our high knowledge of particle detectors and ionizing radiation to apply radiography and emission tomography and neutron detection to different fields of industry, but we also naturally carry out different simulations that help us develop each of our solutions more efficiently.
FORGED RODS IN CONCRETE COLUMNS![]()
If the concrete is well made, the slab should not rust due to the basic environment generated by the concrete. However, in the event of cracks or fissures, oxidation or corrosion could occur, reducing the useful section of the structural element. To detect these effects by neutron emission, we simulate metal rods embedded in a concrete column and irradiate them from different positions with neutrons of energies compatible with portable generators.
We simulated 4 steel rods in a concrete column, two with a layer of iron oxide (Fe2O3) of 4 mm which reduces their effective cross-section. Thanks to the increased interaction of neutrons with oxygen, the rust is clearly identified with our technology. In backscatter images, both rods and the oxide layer are distinguished without the detector being behind the object. In addition, the radiograph of transmission at one second irradiation allows to estimate the cross-section of the rods, detecting possible signs of corrosion or oxidation.

Simulation of a concrete column containing 4 steel rods of 4 cm diameter, two of them with 4 mm of iron oxide. Simulated image of the section of the concrete column with rods obtained by retro-dispersion, that is, the neutrons which have been bounced out 180º after irradiation are detected. Steel rods and oxide coating are identifiable due to different interaction with neutrons.
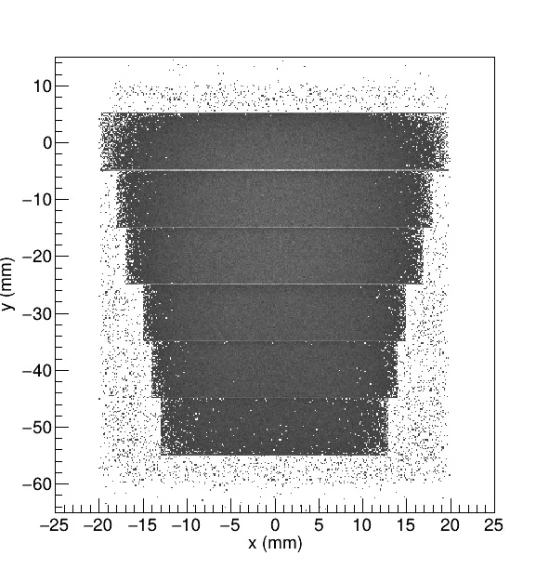
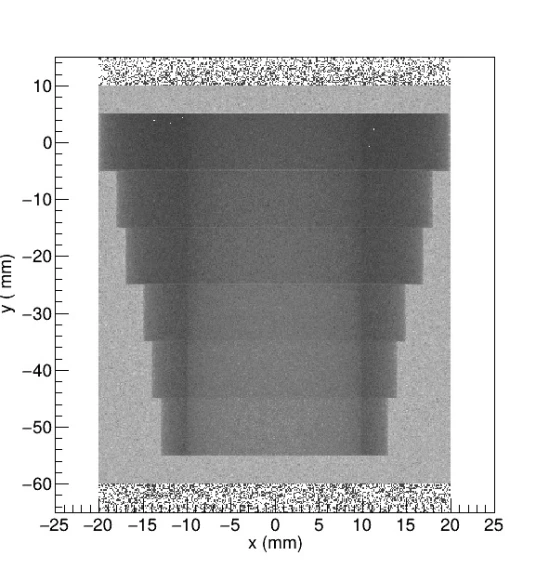
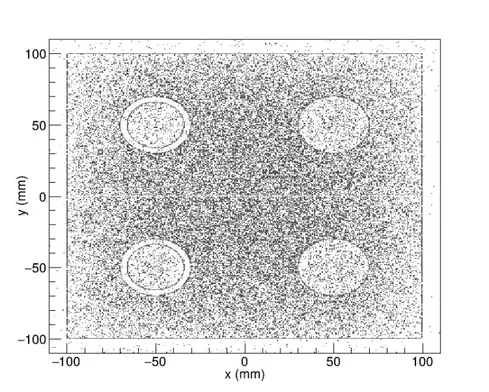
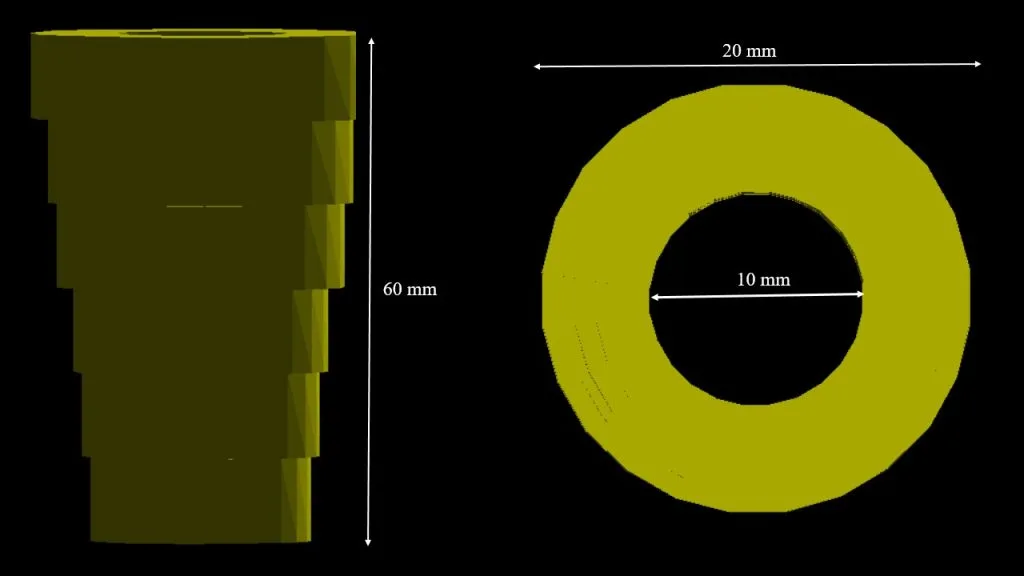
STEEL PIPE WITH DIFFERENT THICKNESSES![]()
The simulated steel pipe containins air inside, with an internal radius of 10 mm and an external radius decreasing in different steps from 20 mm (corresponding to 10 mm wall thickness) to 13 mm (corresponding to a wall thickness of 3 mm). The radiography of the object was simulated both in the open air and in the field, in two different situations: on a concrete block and on a ground block.
The radiographic image by transmission after 1 second of irradiation of the buried pipe in concrete and ground shows a very similar behaviour. The main difference between the two situations is the higher moisture content of the soil and, therefore, higher hydrogen and oxygen content, both elements with high neutron absorption power. In both situations the buried pipe is distinguished by its different wall thicknesses and even, especially in the case of concrete, the different densities are seen to inform the inside of the pipe, in this case a hollow containing air.